



The configuration of PPPoE servers and introduction to IPv6 is described in two articles. Please read them if you want to configure the ISP part first:
This article shows examples of 3 different CPEs from 3 other vendors. We have selected IPv6 routers that are used in networks of Splynx customers. Models of the home routers IPv6 are TP-Link 450, Nucom 8800AC, and Mikrotik, any RouterOS based router.

Below is a typical CPE or Home router connection scheme to the ISP with PPPoE and IPv6 enabled. Let’s take a look at the setup. There are two interfaces configured – one is a WAN that connects to uplink. The second is a LAN interface that usually works as a bridge unit for all physical LAN interfaces – Ethernet and WiFi.
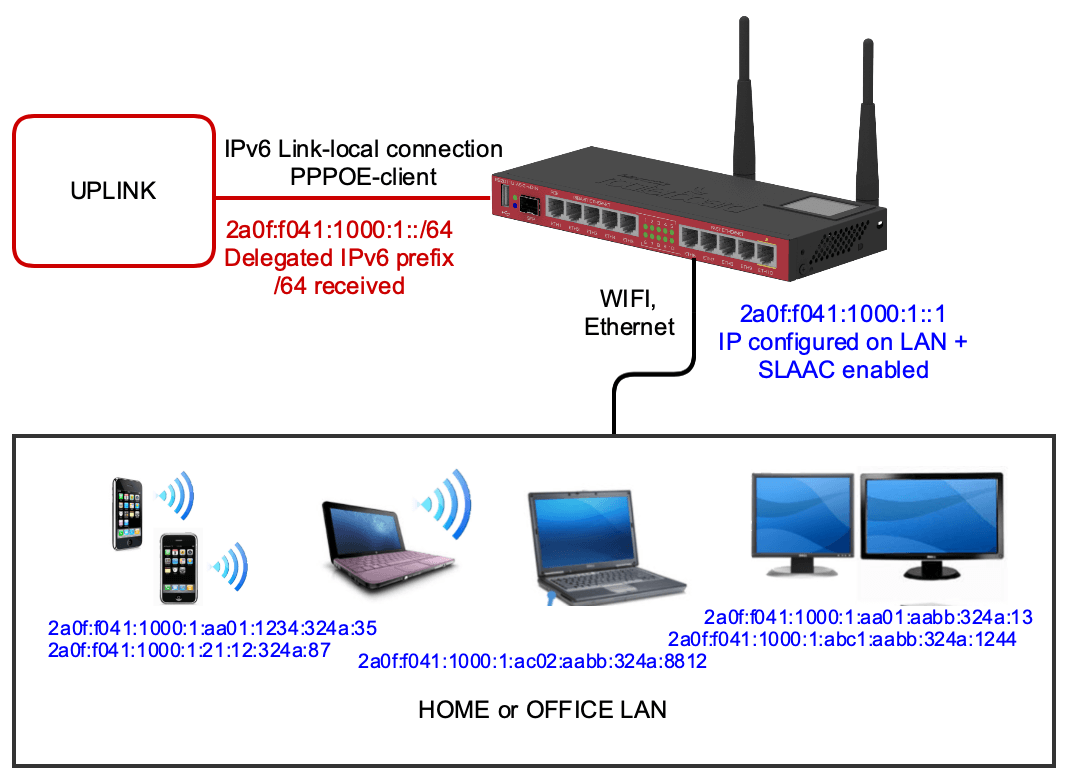
The uplink interface is configured with the PPPoE client. PPPoE client connects to PPPoE server, and communication between the Home router and ISP router works on IPv6 Link-Local addresses. It’s also possible to assign a public IPv6 address to the Home router. We don’t use it in our configs to not make it too complicated. Public IPv6 on a router will be available on the LAN interface, and this IP can be used to access the router.
When the PPPoE Client connection is established, our home router receives an IPv6 LAN prefix called Delegated IPv6 prefix. The home router should configure the IPv6 address on its LAN interface, which will work as a default gateway for all our devices.
When IPv6 on LAN is configured, our router should start announcing IPv6 to the LAN network (similar to what DHCP does in the IPv4 world). The LAN environment is almost always used an IPv6 Stateless auto configuration called SLAAC and is based on the IPv6 Neighbor Discovery protocol (ND).
The router has established a PPPoE connection in the picture above and received a /64 IPv6 pool 2a0f:f041:1000:1::/64. This pool will be used for LAN devices, and all devices will create their own IPv6 addresses from that pool.
As you remember, while IPv4 is a 32 bit IP address that is split into four octets, IPv6 address is 128 bits and is split into eight parts, each containing 16 bits of information. 16-bit parts that contain only zeros can be merged with :: symbols. It means that the network, 2a0f:f041:1000:1::/64 that is allocated to router is equal to 2a0f:f041:1000:1:0:0:0:0:/64, but we cut last 4 zero parts and make view of IP network shorter.
The home router uses the first IP from the received /64 pool in our example. It means that automatically it assigns IP ::1 to its LAN interface. This setup is available in Mikrotik routers. Other routers will automatically generate IP on their LAN interfaces. So, in the case of Mikrotik, IP 2a0f:f041:1000:1::1 is used on the LAN interface, and this IP will become a default gateway for all home devices.
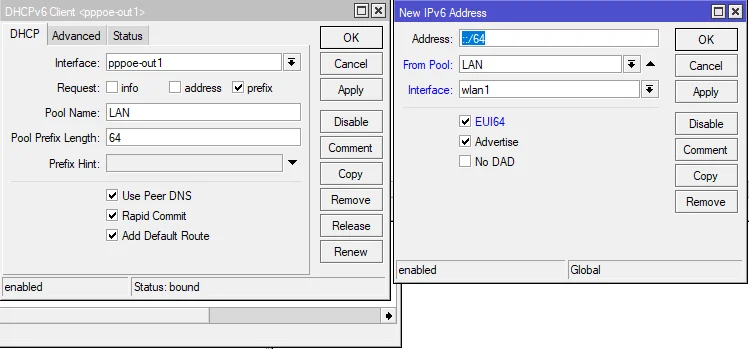
Home devices with IPv6 support have SLAAC enabled on their Internet interfaces, get the IPv6 ND information and create their IPv6 address. The following example shows the configuration of Mikrotik RouterOS. The window on the left side shows PPPoE client interface configuration – we say it’s needed to get a prefix from the PPPoE server. The received prefix is called LAN and is stored in IPv6 pools. The second window shows that the IPv6 address is configured on LAN Interface from the prefix LAN, and EUI64 will be used to create an IPv6 LAN address. Important is flag “Advertise,” which enables SLAAC and ND on the interface so that end devices will get IPv6.
If we want to use IP 2a0f:f041:1000:1::1 on the LAN interface instead of ugly generated IP, disable EUI64 and set up IP as in the example below.
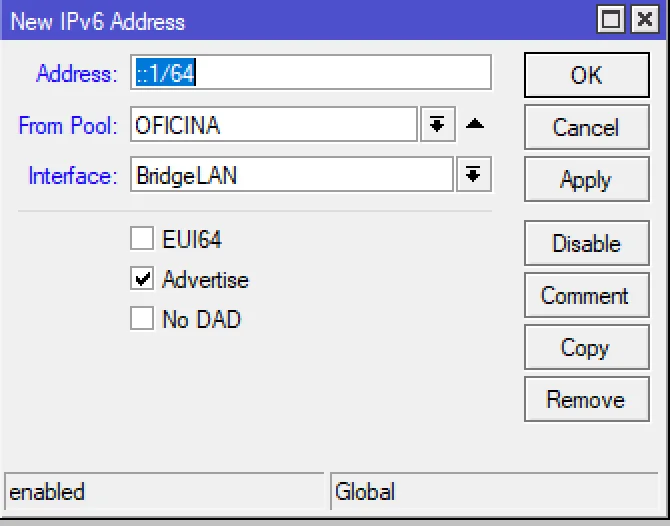
The Mikrotik CPE/Home router is configured, and devices will access the IPv6 internet.
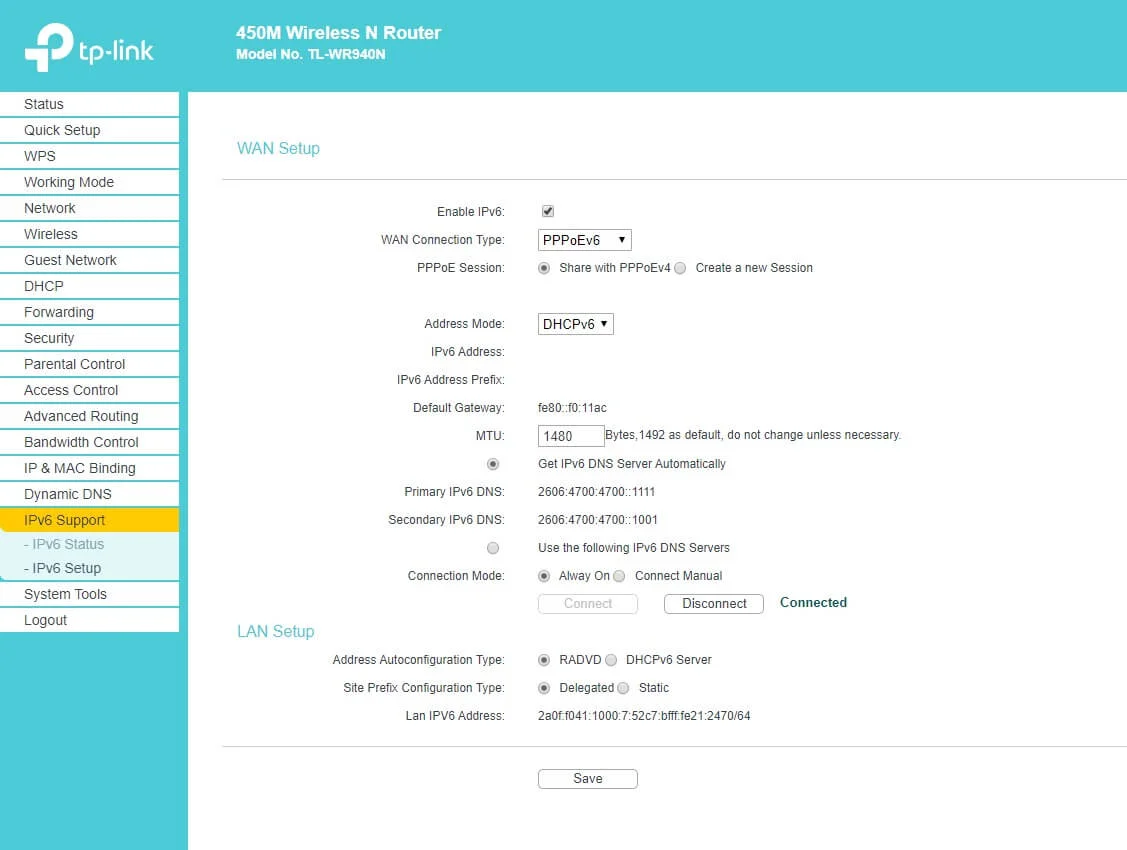
Let’s check the configuration of TP-Link. Setup is much simpler compared to Mikrotik. We must be sure that Firmware supports Ipv6. Many older TP link devices can’t work with IPv6. But the devices that support IPv6 are configured similar way as Mikrotik – enable IPv6 on PPPoE interface, and it will create IPv6 address on LAN with SLAAC allowed.
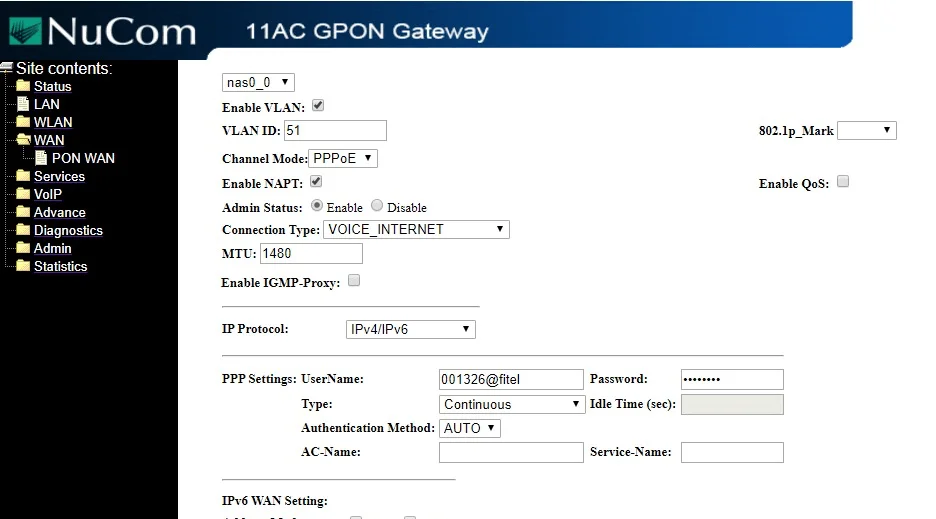
Nucom 8800AC Fiber ONT router has a similar one-step configuration, PPPoE with IPv6 enabled, IPv6 is configured on LAN, and SLAAC enabled to connect end-user devices.
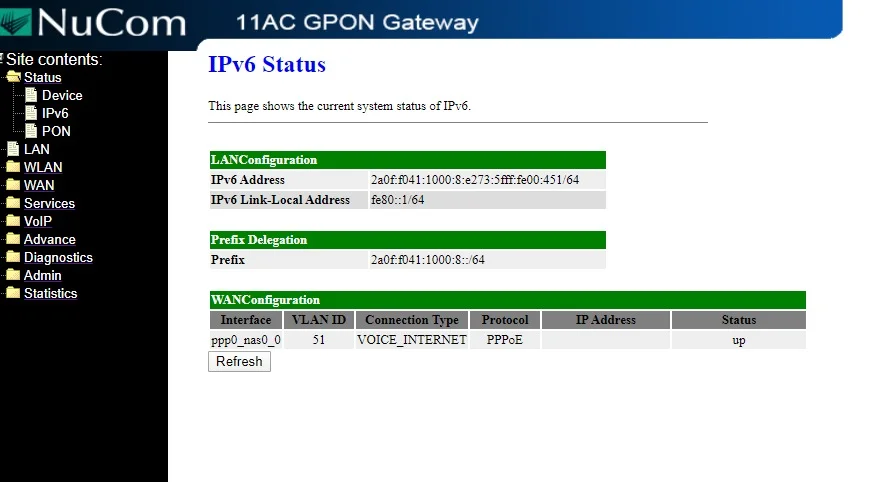
And the configuration of NUCOM is shown below.
Find out how Splynx helps ISPs grow
Learn more