



Splynx provides the feature of contention or aggregation. This feature is used when ISP sells to the end-users services with contention rates for example 1:5, 1:10, etc. Contention means that the end-user will share the bandwidth with other end users in his group.
Splynx operates with two types of contention: Per plan-based and per router contention.
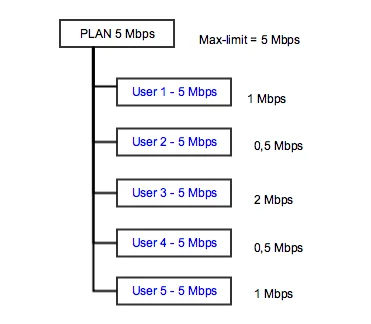
Let’s take a look at the example. We are selling to the end users plan 5 Mbps with a contention rate of 1:5. It means, that Splynx will set up the parent speed limit of 5 Mbps and under this parent, it will place 5 users with a speed limit of 5 Mbps each. What will happen in this situation: if the line is free and one user starts to download/upload, he gets full 5 Mbps throughput. In case, when the second user actively starts downloading, they will get 2,5 Mbps each. When all 5 users will simultaneously download with maximum speed, they will share the bandwidth.
It’s described in the image below:
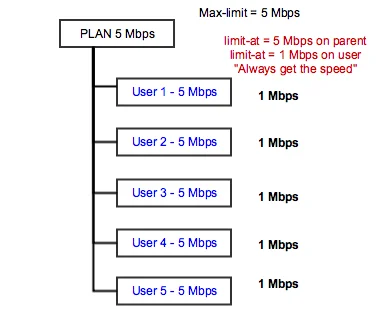
We can tune a bit sharing of speed with setting up “Limit-at” or guaranteed speed. If we place 1 Mbps to each user, then all users will always get at least 1 Mbps.
In that case, all 5 users will simultaneously download with 1 Mbps speed. It’s shown in the second screenshot.
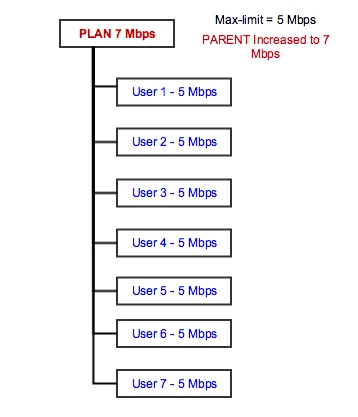
What will happen in the situation, when we will put 7 users on the 1:5 contention plan? Splynx will change the parent speed to 7 Mbps in this particular case but will leave the maximum speed of each user at 5 Mbps.
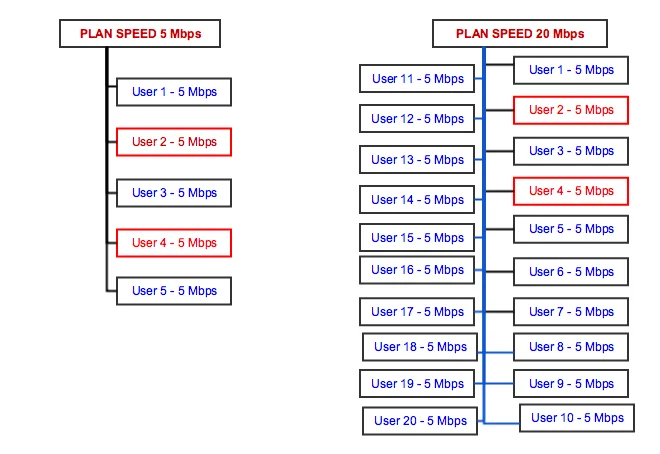
If you are planning to deploy plan-based contentions, use them on central routers to achieve high amounts of users in one tree. Compare two situations – 1:5 contention tree with 5 users and two of them are hard downloaders, it means that 3 other users will never get 5 Mbps speed because they are all under one common parent of 5 Mbps.
If we place 20 users on this contention 1:5, then the parent maximum speed will be set to 20 Mbps and then two or more high downloaders will not use the whole bandwidth.
Router-based contention is used in this scenario:
Imagine that we have a wireless AP which is connected to a backbone network with 30 Mbps speed. But we connected to that AP users with a total possible bandwidth of 60 Mbps. What can happen in a peak time is that users will consume more traffic than can be sent through the uplink. It means that wireless links can become overutilized and unstable. It’s shown in the picture below.
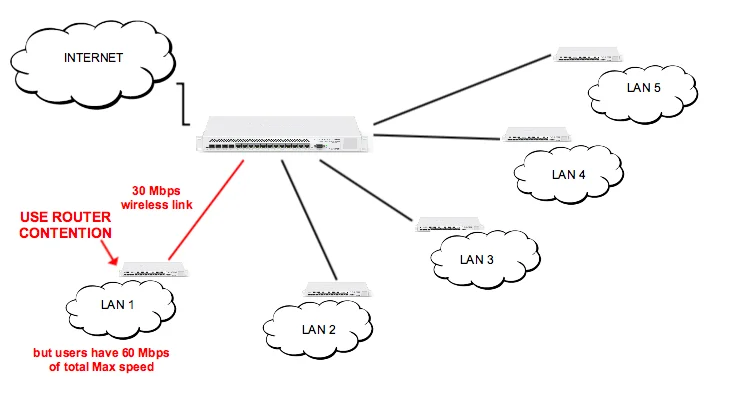
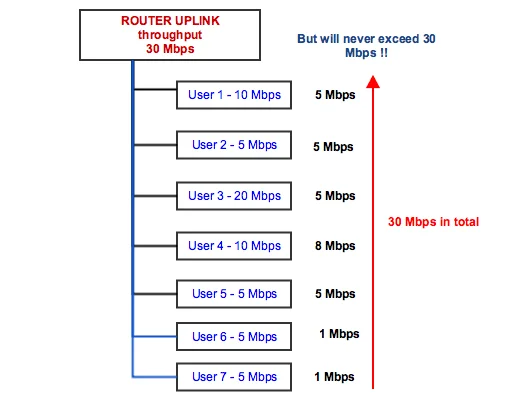
To prevent this situation, router-based contention can be used. In Splynx each router has the field “Sector/Speed limits”, where can be defined groups and the administrator can put users under these groups. As a result, we will achieve contention per router :
In a short video tutorial you can find how to configure Splynx and plan-based contention:
Configuration of the Router-based contention is shown on another video:
Find out how Splynx helps ISPs grow
Learn more