



Splynx provides a robust RADIUS suite for centralized network access administration and delivery of central AAA-based services to customers. However, what happens if your NAS device cannot reach the Splynx RADIUS server or process AAA how you expect it to?
In this article, we will address common network connectivity problems between NAS and Splynx Radius service, and provide solutions to locate and troubleshoot them efficiently.
Examples in this article will use MikroTik as the NAS device because they are the most commonly used by our clients. Nevertheless, the network troubleshooting approaches discussed are applicable to other vendors as well.
First and foremost, it’s important to note that Splynx’s RADIUS server listens on all network interfaces available on the Ubuntu Server and utilizes port 1812/udp for user authentication and port 1813/udp for online session accounting.
You can also configure the incoming RADIUS protocol on your NAS (usually 3799/udp) to allow Splynx to change online user session parameters by sending a CoA or reconnect your users by sending a PoD packet to the router.
We will examine the most common and concerning problem – RADIUS timeout:
![]()
Most likely, RADIUS protocol packets originating from your router do not reach the server or the server replies fail to return to the router.
We can suggest you to start checking basic network connectivity from NAS side with ICMP-based utilities like Ping or Traceroute:
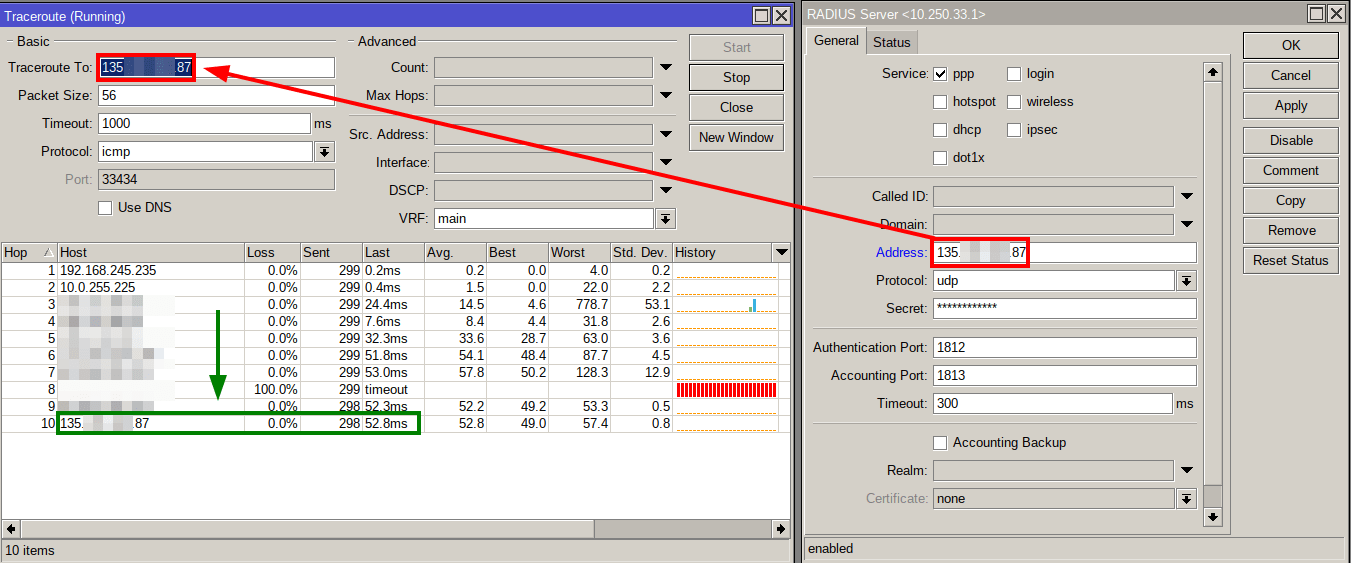
The traceroute utility can help you quickly identify potential problems along the entire route of packets traveling between the two hosts.
However, the issue might be specifically with connecting to the UDP ports 1812 or 1813 that the RADIUS server uses. Unfortunately, many devices, including MikroTik, do not have tools like Nmap to scan UDP ports.
If there are no connectivity problems with ICMP and the server, there are most likely some firewalls that are preventing RADIUS packets from getting through at some point.
To review firewall rules on MikroTik devices, navigate to the “IP -> Firewall” menu. Ensure that there are no rules that reject or drop UDP packets on RADIUS ports, or any invalid NAT rules that may incorrectly translate the source or destination addresses in packets.
From the Ubuntu Server side on which your Splynx instance is running, firewall rules that are active on the system can be checked by executing the following commands: “sudo ufw status” and “sudo iptables -L”.
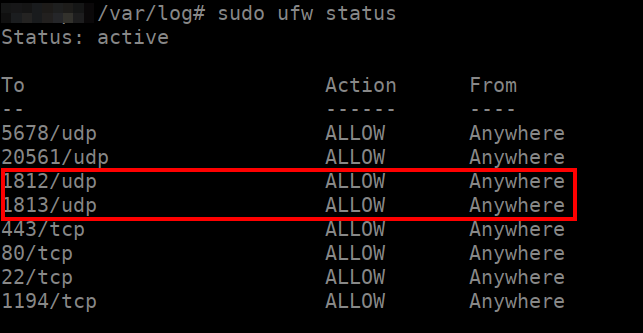
The article about the UFW (Uncomplicated Firewall) tool may be helpful if you’re new to Ubuntu/Linux firewalls.
It’s worth mentioning that in certain cases, network issues may arise that cannot be resolved by yourself when connecting to the Radius over the Internet. It is recommended to contact your upstream provider in such situations for assistance with troubleshooting network issues.
A possible reason for the timeout error may be due to a mismatch between the RADIUS secret or Src. Address configured on your NAS and Splynx “Networking -> Routers” entry. To address this connectivity issue, go to the “Networking -> Routers” section on the Splynx admin portal and compare the connection password and NAS IP with the settings in the router’s RADIUS client configuration as displayed below:
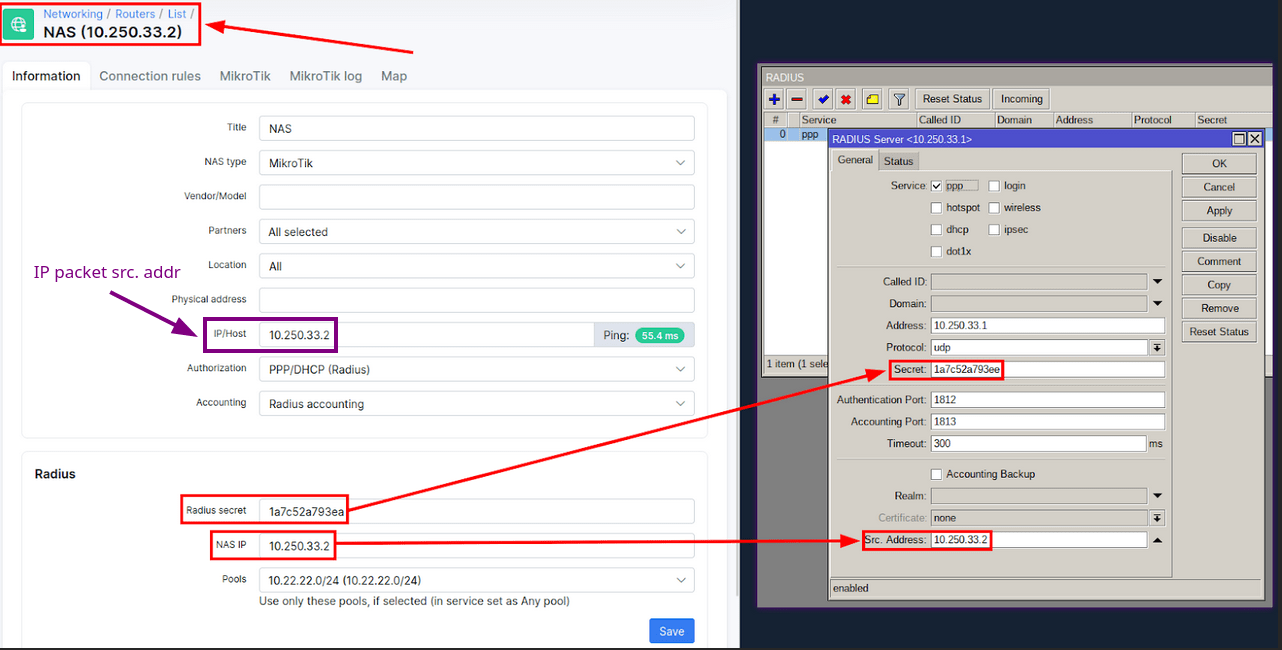
It is important to note that a mismatch in the source address of IP packets sent by the router to the RADIUS server can cause a timeout error.
This may occur if there is NAT between your NAS and RADIUS server, which may translate the source address of IP packets to a different one than what is entered in the “Networking -> Routers -> IP/Host” field. In such cases, the RADIUS server will ignore the packet, resulting in a timeout.
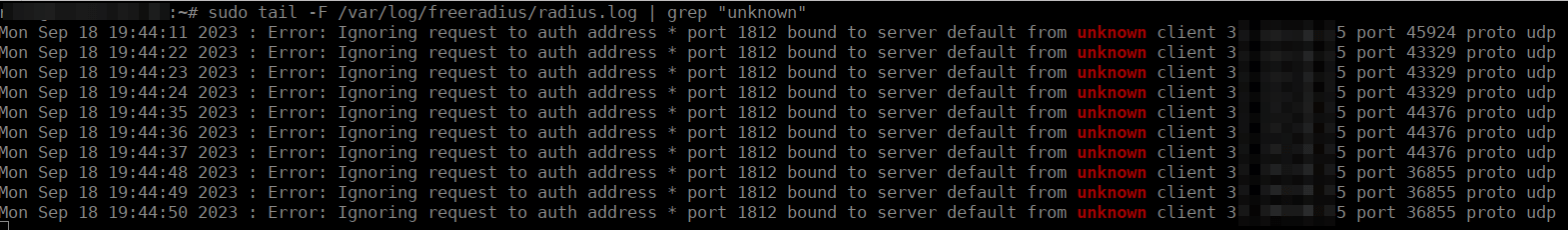
The most convenient way to check is by reviewing live logs of freeRADIUS from the Ubuntu Server CLI where Splynx is located using the command:
sudo tail -F /var/log/freeradius/radius.log | grep “unknown”
To address NAT concerns and increase connection security, we highly recommend using the built-in OpenVPN feature provided by Splynx.
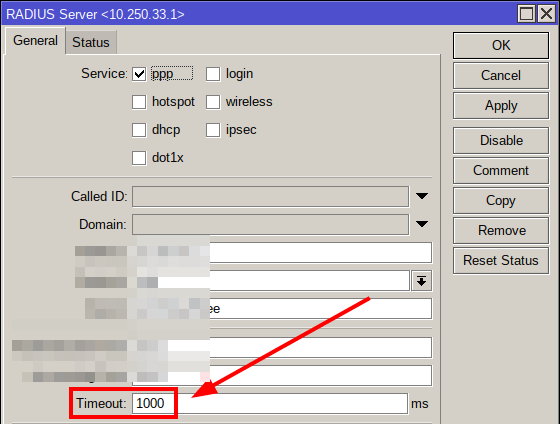
By default, the timeout setting in the MikroTik RADIUS client is set to 300ms, which could be too low if there are latency issues with the network connection between two hosts, or if RADIUS is struggling to process router requests in time.
To overcome these problems, you may want to consider increasing the client timeout setting to a higher value:
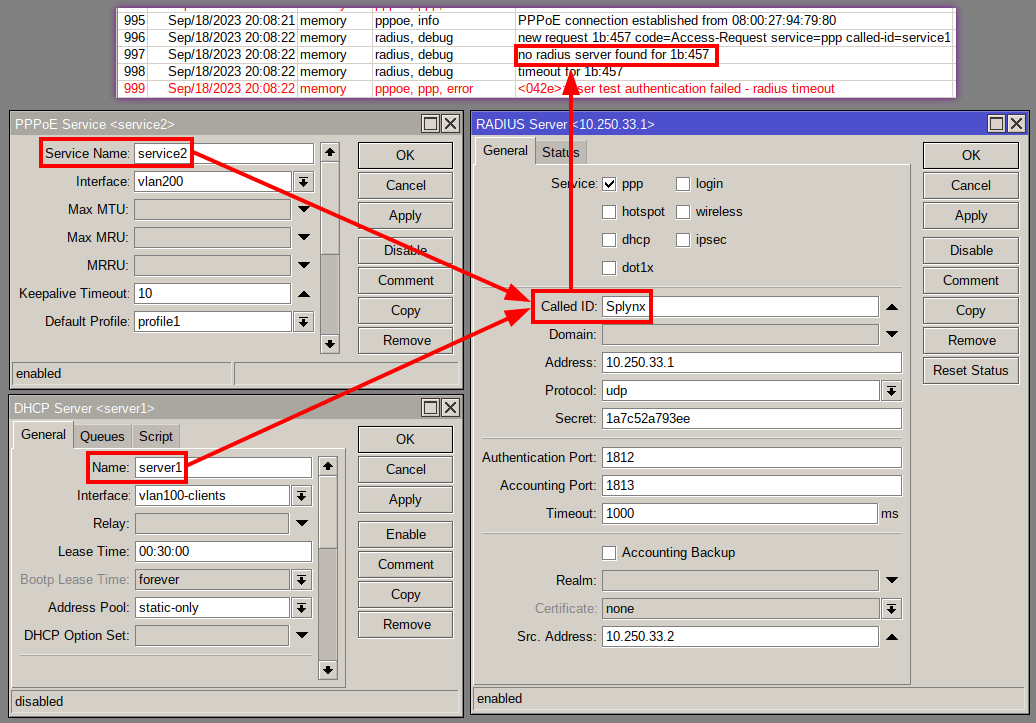
Using the “Called ID” setting in your MikroTik RADIUS configuration, you can designate certain services on your NAS to be processed by the RADIUS server entry that matches the service name, which is mainly used in multiple RADIUS server setups.
However, if there is a mismatch between the PPP/DHCP/Hotspot service names and the RADIUS server “Called ID” entry, the router will not be able to find a matching RADIUS server, resulting in a timeout error as displayed on the image below:
Although unlikely to occur if your Ubuntu Server meets Splynx’s recommended hardware requirements and there are no critical hardware issues that could affect overall server operability, there is still a possibility that Splynx RADIUS services may not function correctly. To gain more detailed information on how to troubleshoot Splynx RADIUS and MikroTik, please refer to the following article: Troubleshooting RADIUS.
It is worth noting that version 4.1 includes the ability to seamlessly set up RADIUS failover to increase the redundancy of AAA processes in your network.
Find out how Splynx helps ISPs grow
Learn more